
Saoudi N, Cosío F, Waldo A, Chen SA, Iesaka Y, Lesh M, Saksena S, Salerno J, Schoels W Working Group of Arrhythmias of the European of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Rob Orman ERCast – Atrial Flutter, Fibrillation and Ablation (podcast). In contrast, atrial fibrillation will be completely irregular, with no patterns to be discerned within the R-R intervals.  Look for identical R-R intervals occurring sporadically along the rhythm strip then look to see whether there is a mathematical relationship between the various R-R intervals on the ECG. assuming an atrial rate of 300bpm (P-P interval of 200 ms), the R-R interval would be 400 ms with 2:1 block, 600 ms with 3:1 block, and 800 ms with 4:1 block In atrial flutter with variable block the R-R intervals will be multiples of the P-P interval - e.g. Atrial flutter will not usually cardiovert with these techniques (unlike AVNRT), although typically there will be a transient period of increased AV block during which flutter waves may be unmasked. Turn the ECG upside down and closely examine the inferior leads (II, III + aVF) for flutter waves. Narrow complex tachycardia at 150 bpm (range 130-170)? Yes -> Suspect flutter!. Handy Tips For Spotting Flutter Rapid Recognition AV block is a physiological response to rapid atrial rates and implies a normally functioning AV node. The term “AV block” in the context of atrial flutter is something of a misnomer.
Look for identical R-R intervals occurring sporadically along the rhythm strip then look to see whether there is a mathematical relationship between the various R-R intervals on the ECG. assuming an atrial rate of 300bpm (P-P interval of 200 ms), the R-R interval would be 400 ms with 2:1 block, 600 ms with 3:1 block, and 800 ms with 4:1 block In atrial flutter with variable block the R-R intervals will be multiples of the P-P interval - e.g. Atrial flutter will not usually cardiovert with these techniques (unlike AVNRT), although typically there will be a transient period of increased AV block during which flutter waves may be unmasked. Turn the ECG upside down and closely examine the inferior leads (II, III + aVF) for flutter waves. Narrow complex tachycardia at 150 bpm (range 130-170)? Yes -> Suspect flutter!. Handy Tips For Spotting Flutter Rapid Recognition AV block is a physiological response to rapid atrial rates and implies a normally functioning AV node. The term “AV block” in the context of atrial flutter is something of a misnomer. 
Atrial flutter with 1:1 conduction is associated with severe haemodynamic instability and progression to ventricular fibrillation.The administration of AV-nodal blocking agents to a patient with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome can precipitate this Atrial flutter with 1:1 conduction can occur due to sympathetic stimulation, or in the presence of an accessory pathway.Higher-degree blocks can occur - usually due to medications or underlying heart disease - resulting in lower rates of ventricular conduction, e.g.The most common AV ratio is 2:1, resulting in a ventricular rate of ~150 bpm Ventricular rate is determined by the AV conduction ratio (“degree of AV block”).
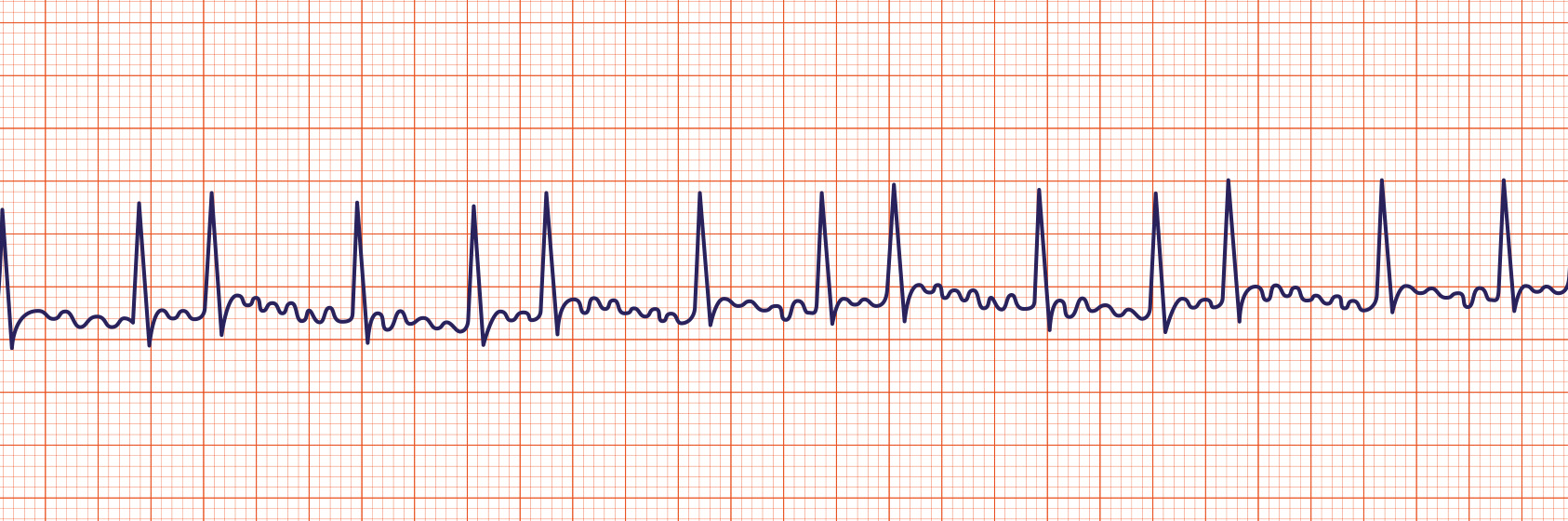
The length of the re-entry circuit corresponds to the size of the right atrium, resulting in a fairly predictable atrial rate of around 300 bpm (range 200-400) Atrial flutter is a form of supraventricular tachycardia caused by a re-entry circuit within the right atrium.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
